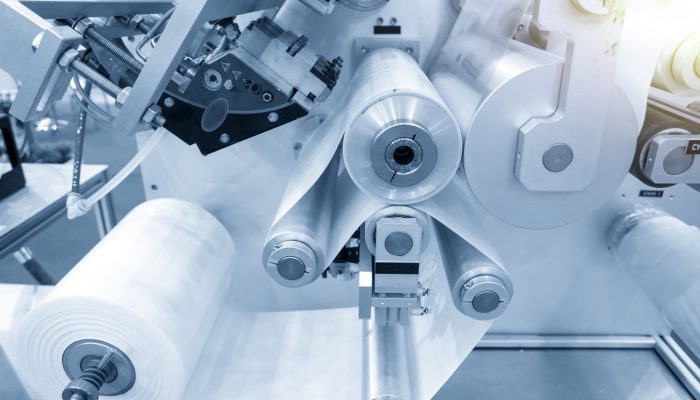
Many industries utilize plastic extrusion to create a wide variety of plastic products, ranging from containers used in the food and medical sectors to PVC pipes and insulation materials used in construction, as well as electronic cable insulation. The extrusion process involves several components including a drive motor and gearbox, feeding system, extruder barrel, screw, die and cutting system. This process melts plastic material in the heated extruder barrel and with a rotating lead screw, forces it through a mold or die, at the end of the extruder barrel, to form a specific profile.

Benefits of Equipment Alignment
Proper alignment of these components is crucial for producing consistent, uniform, high-quality products while minimizing wear. Misalignment in the extrusion line can cause variations in part thickness, shape, and surface texture. When components are aligned correctly, equipment operates smoothly, producing parts with consistent dimensions and quality.
Additionally, well-aligned equipment helps avoid unnecessary friction and wear, which can extend the lifespan of machinery and prevent costly repairs and downtime. Aligned equipment operates more efficiently, requiring less energy to produce the same output. Calibration and adjustment become easier, allowing for quicker machine setups and product changeovers, which enhances production efficiency.
Misalignment Concerns
Many users of plastic extrusion equipment report concerns regarding the misalignment of the extruder’s barrel with the screw or gearbox. Such misalignment can cause operational and mechanical issues, resulting in poor product quality and potential damage to expensive machine components. When a barrel is not aligned properly with the screw, it can create uneven pressure, leading to localized wear that degrades the screw surface and diminishes performance.
At the same time, if the barrel and screw are misaligned, the gearbox may experience additional strain as it tries to compensate for misalignment. This can lead to overheating and increased energy consumption.
Laser Alignment Solution
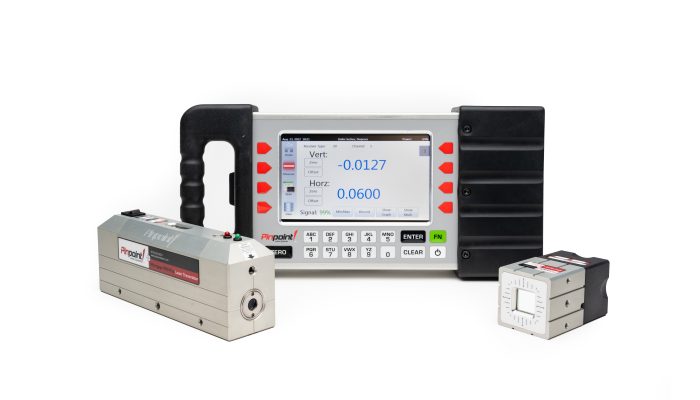
Offset or concentricity misalignments occur when the centerline of the rotating gearbox shaft and screw is misaligned with the barrel. Laser alignment systems can precisely and quickly evaluate the alignment of the lead screw, in both vertical and horizontal axes, relative to the inside of the extruder barrel to verify alignment. Offering better measurement accuracy and user-friendly operations compared to conventional alignment devices or methods, laser alignment systems provide rapid information, accurate, and quantitative results on gearbox, screw, and extruder barrel alignment and wear.
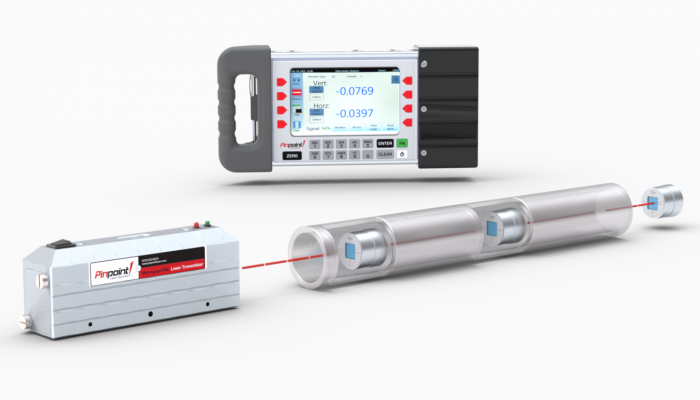
How Laser Alignment Works
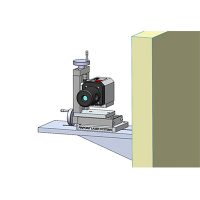
When using a laser alignment system to align single or dual barrel extruder barrels, a laser transmitter emits a reference beam down the length of the barrel to a receiver that measures the position of the beam to determine alignment of the extruder. The receiver connects to a display for real-time readings and/or a laptop that records data, using software to determine concentricity and offset to bring the extruder barrel and screw back into alignment.
Both the laser transmitter and receiver can be used with custom mounts, with the laser positioned on the gearbox shaft and receiver at the end of the barrel. They work in unison to take measurements in various orientations, allowing for the detection of offset errors. By measuring at both ends of the extruder barrel, and comparing these measurements, the extruder barrel and interior screw can be aligned for parallelism. Measurements can be repeated to determine very small tolerances.
Properly aligned plastic extrusion machinery offers operational advantages that contribute to quality output, efficiency and reduced maintenance. Laser alignment systems help identify the necessary required to align equipment components effectively.